| SKU | MS.1938 |
|---|---|
| Circa | 1700 AD to 1900 AD |
| Medium | Bronze |
| Origin | Near Eastern |
| Gallery Location | UK |
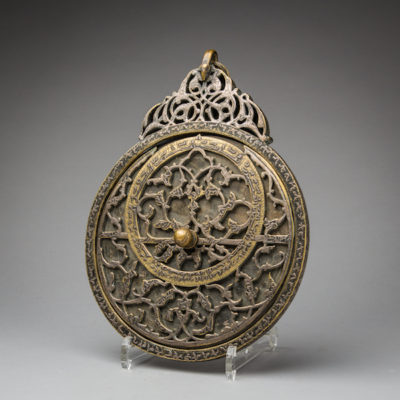
An astrolabe is an elaborate inclinometer, historically used by astronomers and navigators to measure the inclined position in the sky of a celestial body, during the day or during night- time. In consequence it was used to identify stars or planets, to determine the local latitude based on the local time, and vice versa. It was extensively used during the classical antiquity, from where the use of astrolabes spread further and it became an extremely popular instrument during the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and Renaissance periods, its many uses including timekeeping, astrology and surveying. The word is an ancient Greek composite, deriving from the words astern, “star”, and the verb lamvanein, “to take”, in this case used in the sense of “reading, perceiving”. Astrolabes, or an early archetype of them was first invented and used during the Hellenistic period, mostly employed in resolving problems concerning astronomy and for astronomical studies Astrolabes continued in use in the Greek-speaking world throughout the Byzantine period. The Christian theologian and philologist John Philoponus of Alexandria wrote around 550 AD. a treatise on the astrolabe in Greek, which is the earliest extant treatise on the instrument. Severus Sebokht, one of the leading figures of ecclesiastical, philosophical, and scientific culture of late antique Syria, also wrote a treatise on the astrolabe in the Syriac language in the mid-7th century. Sebokht refers to the astrolabe as being made of brass in the introduction of his treatise, indicating that metal astrolabes were known in the Christian East well before they were developed in the Islamic world or in the Latin West. Islamic astronomers primarily used astrolabes for astronomical studies and developed it further, chiefly employing it as an aid to navigation and also as a way of finding the qibla, the direction to the Mecca, the times of sunrise and the rising of fixed stars, as to help schedule morning prayers (salat). The 8th century mathematician Muhammad al-Fazari is the first person credited with building the astrolabe in the Islamic world. The astrolabe is effective for determining latitude on land or calm seas, although it is less reliable on the heaving deck of a ship in rough seas. The mariner's astrolabe was developed to solve that problem. The geared mechanical astrolabe was invented by.Abi Bakr of Isfahan in 1235. In 1370, the first Indian treatise on the astrolabe was written by the Jain astronomer Mahendra Suri. The astrolabe of Barcelona, made from brass in tenth-century Spain, 980 AD., is considered the most ancient astrolabe with Carolingian characters that has survived in the Christian Occident and is also the first known metal astrolabe in Western Europe. Metal astrolabes avoided the warping that large wooden ones were prone to, allowing the construction of larger and therefore more accurate instruments. – (MS.1938)
Login to view price
Sign-up to receive the latest Wedding Estates news and promotions!